Understanding AWS instances
AWS instances are virtual servers in the cloud that empower businesses to run applications and host websites without the need for physical hardware. To optimize your AWS experience, it's crucial to comprehend the types of instances available:
Types of AWS instances
- Compute Instances (EC2): These are the fundamental building blocks for running applications on Amazon's cloud infrastructure, offering diverse configurations to meet varying computational needs.
- Storage Instances (EBS and S3): Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) provides scalable block-level storage volumes for use with EC2 instances, while Simple Storage Service (S3) is an object storage service designed for scalability and durability.
Data Stored on AWS Instances
- AWS instances store critical data, including application files, databases, configurations, and user-generated content.
- Understanding the nature of data on AWS instances is vital for devising a targeted backup strategy.
Common risks associated with AWS instances
AWS provides a robust and scalable cloud computing platform, but like any technology, it is not without its risks. Understanding and mitigating these risks is crucial for businesses relying on AWS instances. Here are some common risks associated with AWS instances:
- Accidental Deletion or Modification: Human errors can lead to the unintentional deletion or modification of critical data.
- Hardware Failures: Although rare, hardware failures can occur, potentially leading to data loss if not adequately backed up.
- Security Breaches: Unauthorized access or security breaches can compromise sensitive data, emphasizing the need for secure backup solutions.
- Data Corruption: Software bugs, glitches, or other unforeseen issues can result in data corruption, emphasizing the need for data integrity measures.
Step-by-step guide for AWS backup EC2 instance
Creating a step-by-step guide on how to backup AWS instance involves a systematic approach to ensure the safety and recoverability of your critical data. Follow these steps to backup AWS instance:
1. Log in to your AWS account to access the AWS console.
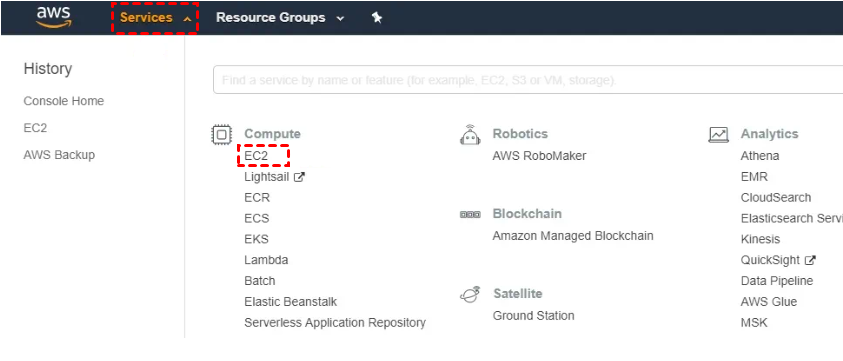
2. Navigate to the top bar and choose Services, then click on EC2 to initiate the EC2 Management Console.
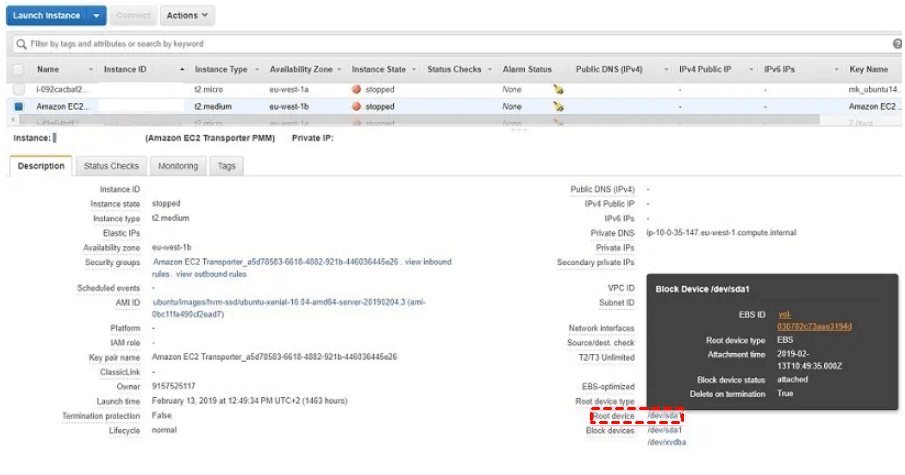
3. Select Running Instances and pick the specific instance you wish to create a backup for.
4. Explore the lower pane to access essential technical details about the instance. In the Description tab, locate the Root device section and click on the /dev/sda1 link.
5. Within the ensuing pop-up window, identify the EBS ID name for the volume and click on it.
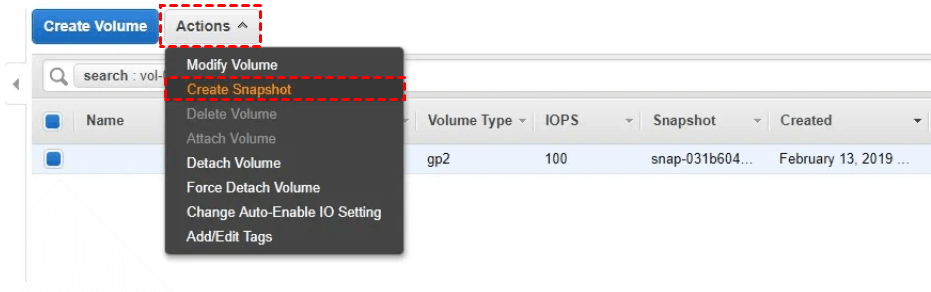
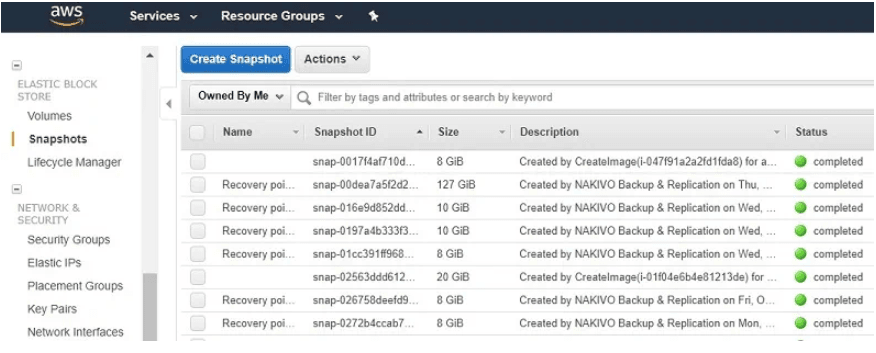
6. Access the Volumes section, click on Actions, and choose Create Snapshot.
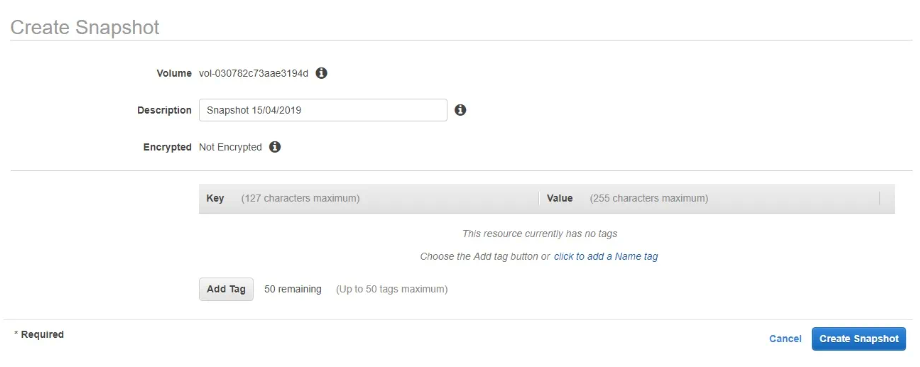
7. In the Create Snapshot box, provide a distinct description for the snapshot and assign tags for streamlined monitoring. Subsequently, click Create Snapshot.
8. Initiate the snapshot creation process, which should conclude swiftly. The duration is primarily influenced by the size of data within your Amazon EBS volume.
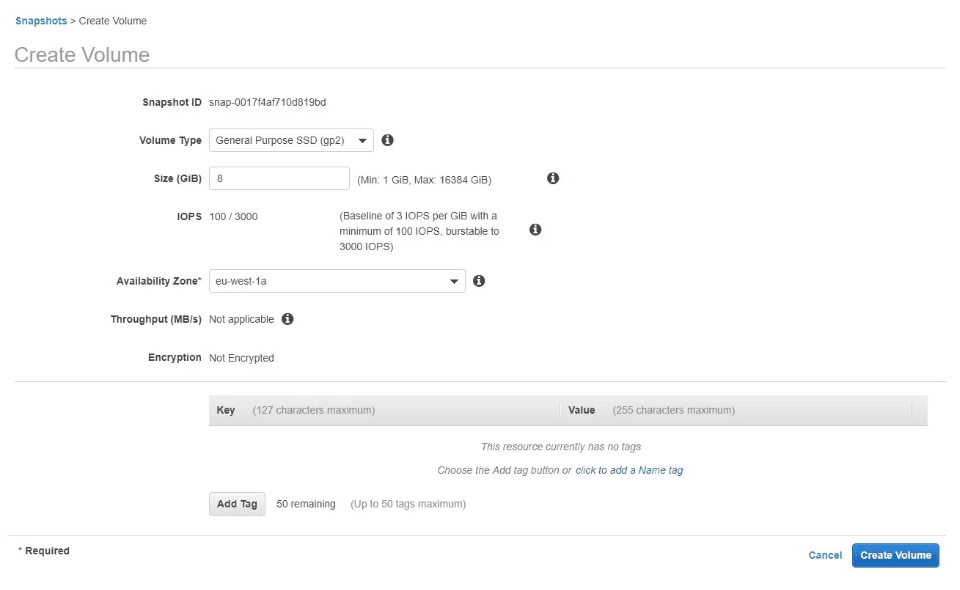
9. To utilize the snapshot for backup, select the corresponding volume snapshot, click on the Actions button above, and opt for Create Volume. Follow the prompts to configure volume details (such as volume type, size, IOPS, availability zone, and tags). Finally, click Create Volume to generate a new volume that can be later attached to the desired AWS EC2 instance.
Free Data Protection: Backup Virtual, Physical and MSSQL to Amazon S3
AOMEI Cyber Backup is a robust solution designed to streamline and secure the backup to AWS. By leveraging Amazon S3, it ensures reliable and scalable storage for your critical data. This integration allows users to seamlessly back up their critical data to Amazon S3, providing an extra layer of protection against data loss. AOMEI Cyber Backup simplifies the backup process with its user-friendly interface, enabling automated backups, scheduling, and management of backup tasks with ease.
With AOMEI Cyber Backup, safeguarding your AWS environment has never been more straightforward and dependable.
FAQs about AWS instance
Q: Can I back up instance metadata and tags?
A: Instance metadata and tags are not included in standard EBS snapshots. To ensure that metadata and tags are backed up, you may need to include scripts or additional processes to capture and restore this information as part of your backup strategy.
Q: How can I monitor the performance of my AWS instances?
A: AWS provides services like Amazon CloudWatch for monitoring EC2 instances. You can set up custom metrics, alarms, and logs to track performance, resource utilization, and other relevant metrics for your instances.
Q: Can I change the instance type after launching it?
A: Yes, you can change the instance type of a running instance. However, the new instance type must be compatible with the underlying hardware. It involves stopping the instance, changing the instance type, and then restarting the instance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding AWS instances, recognizing associated risks, and implementing a strategic “AWS create backup of EC2 instance” plan are integral components of maintaining a resilient and secure digital infrastructure. By following this guide, you can navigate the complexities of AWS instances, fortify your data against potential threats, and ensure the continuity of your operations in the ever-evolving landscape of cloud computing.